학습의 다차원적 이해
학습은 단순한 기억의 축적이 아니라 생물‧심리‧사회‧문화적 차원에서 행동과 지식 구조가 지속적으로 재구성되는 과정이다. 본 보고서는 정의, 역사, 신경과학, 주요 이론, 기술 발달까지 포괄해 학습의 본질을 통합적으로 설명한다. 핵심 결론은 다음과 같다.123
- 인간 학습은 경험을 통해 신경 회로를 가소적으로 재배선하며 인지적 구조를 점진적으로 확장한다.4567
- 20세기 이후 행동주의→인지주의→구성주의→사회‧경험‧연결주의로 이론이 다층화되었다.891011
- 수면, 의미 맥락, 사회적 관찰 등 환경적 조건이 학습 고도화를 좌우한다.121314
- 머신러닝은 대량 데이터 기반의 통계적 일반화로 인간 학습과 상보적이지만 본질적으로 다른 메커니즘을 지닌다.151617
1. 학습의 정의와 핵심 특성
1.1 심리학적 정의
심리학은 학습을 경험 결과로 나타나는 비교적 영속적 행동‧지식 변화로 규정한다. 이는 성장·피로·약물 등 일시적 요인을 제외하고, 반복 경험에 의해 신경 회로가 강화되는 LTP와 대응한다.182619
1.2 신경생물학적 관점
장기기억 형성 시 해마 회로에서 NMDA 수용체 의존성 **장기 강화(LTP)**가 유도되며, 이는 행동적 학습 향상을 예측한다. 수면 중 스피드웨이-리플 이벤트가 학습 직후의 패턴을 재생해 기억을 공고화한다.20132122
1.3 학습 과정의 단계
Bloom Taxonomy는 인지적 학습을 기억→이해→적용→분석→평가→창조 6단계로 계층화한다.2324
Bloom Taxonomy 피라미드 이미지
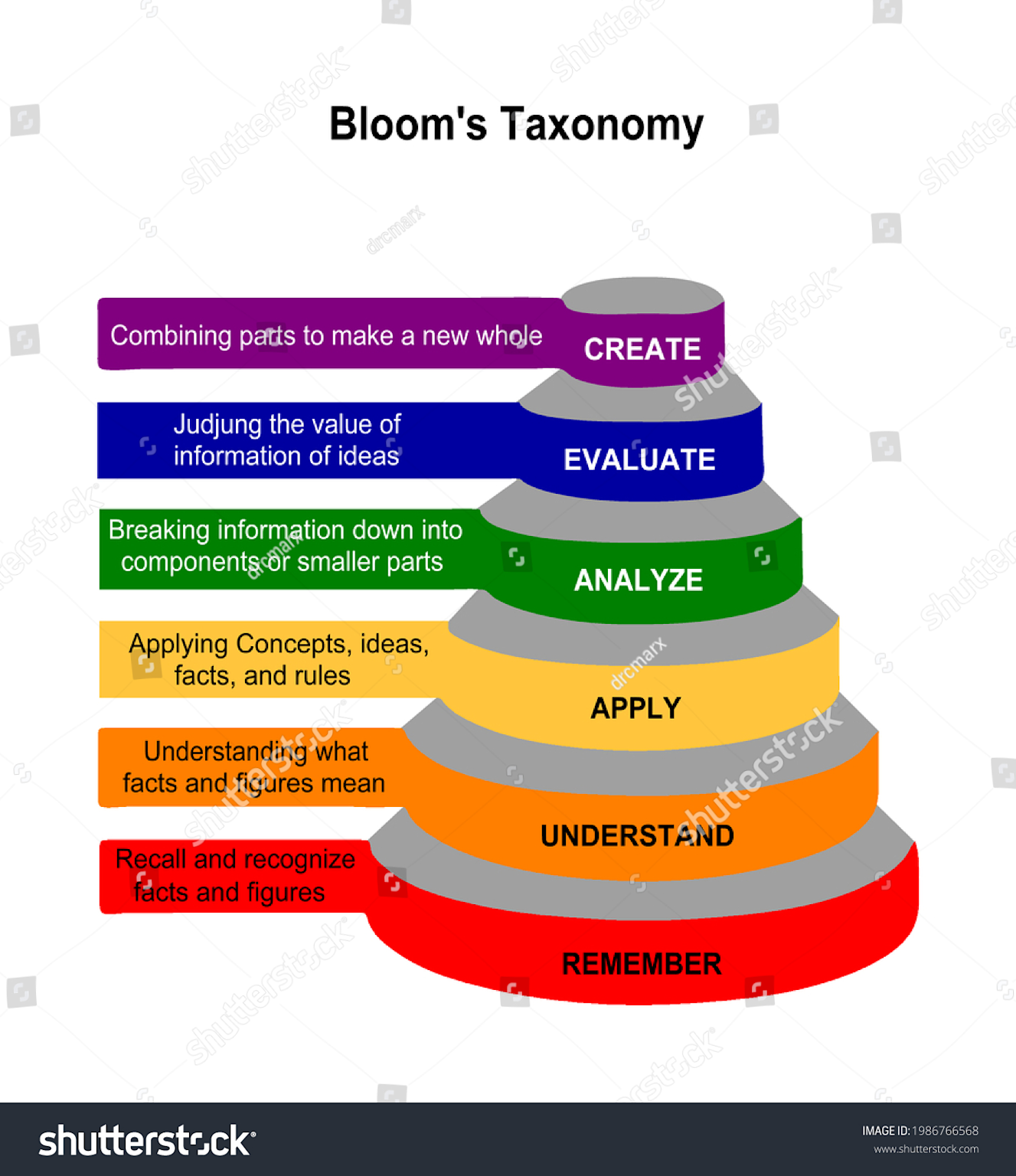
Bloom’s Taxonomy pyramid illustrating hierarchical cognitive processes in learning, from remembering to creating new ideas.
2. 학습이론의 역사적 전개
20세기 이후 주요 학습이론의 등장 연대표는 아래와 같다.
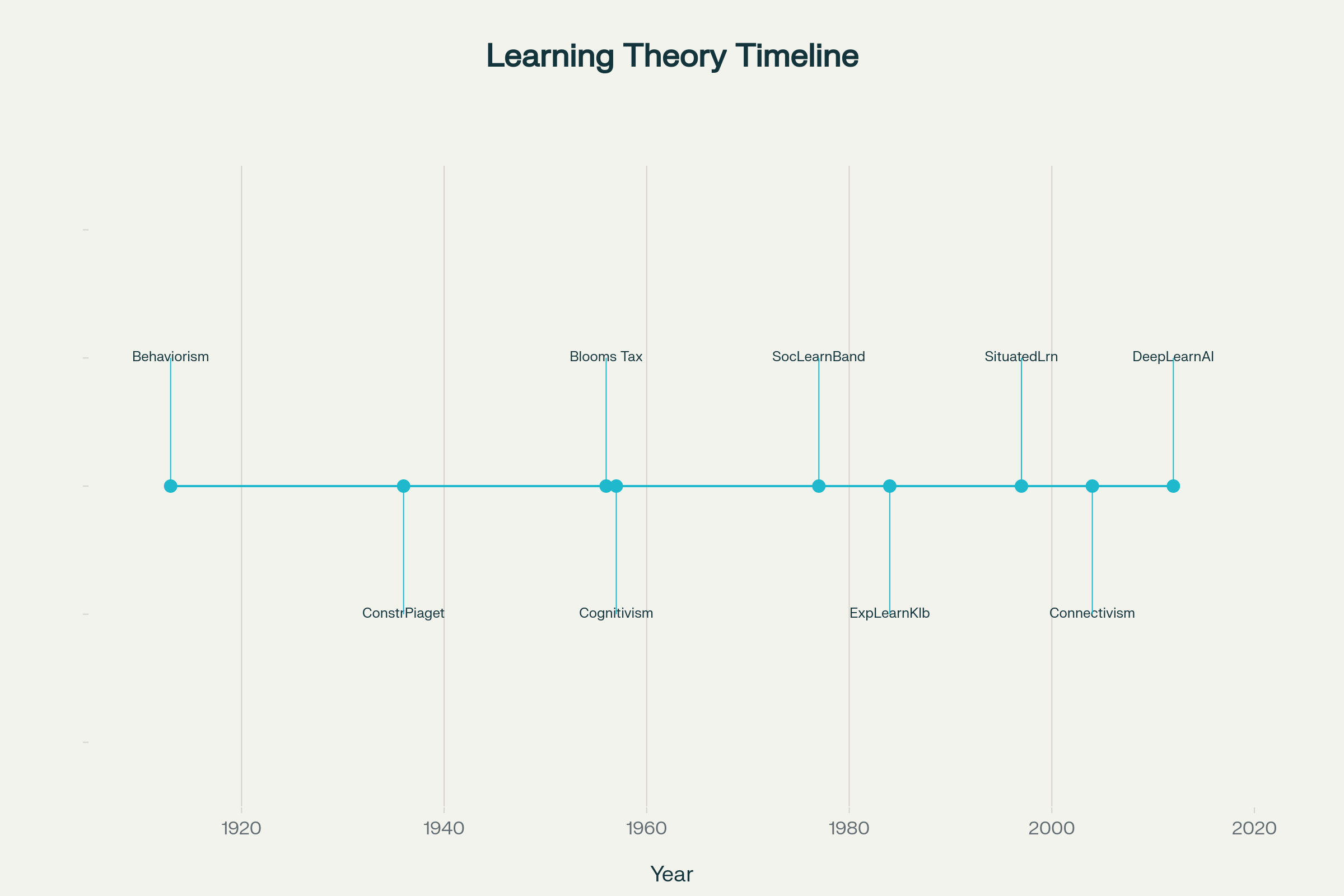
주요 학습이론의 등장 연대표
2.1 행동주의(1913)
왓슨·스키너는 자극-반응 연합과 강화로 행동이 형성된다고 보았다. 학습은 관찰 가능 행동 변화이며 내적 인지는 연구 대상이 아니었다.259
2.2 인지주의(1950s)
톨만·게슈탈트 학자는 정보처리 과정과 인지지도를 강조해 행동주의를 보완했다.52627
2.3 구성주의(1936-)
피아제·비고츠키는 지식은 학습자가 주체적으로 구성하며, 사회적 상호작용과 맥락이 중요하다고 주장했다.282930
2.4 사회 학습(1977)
Bandura는 관찰·모방·모델링을 통해 직접 강화 없이도 학습이 일어난다고 제시했다.123132
2.5 경험 학습(1984)
Kolb는 경험→성찰→추상화→실험의 순환을 통해 지식이 생성된다고 보았다.333435
Kolb 경험학습 주기 이미지
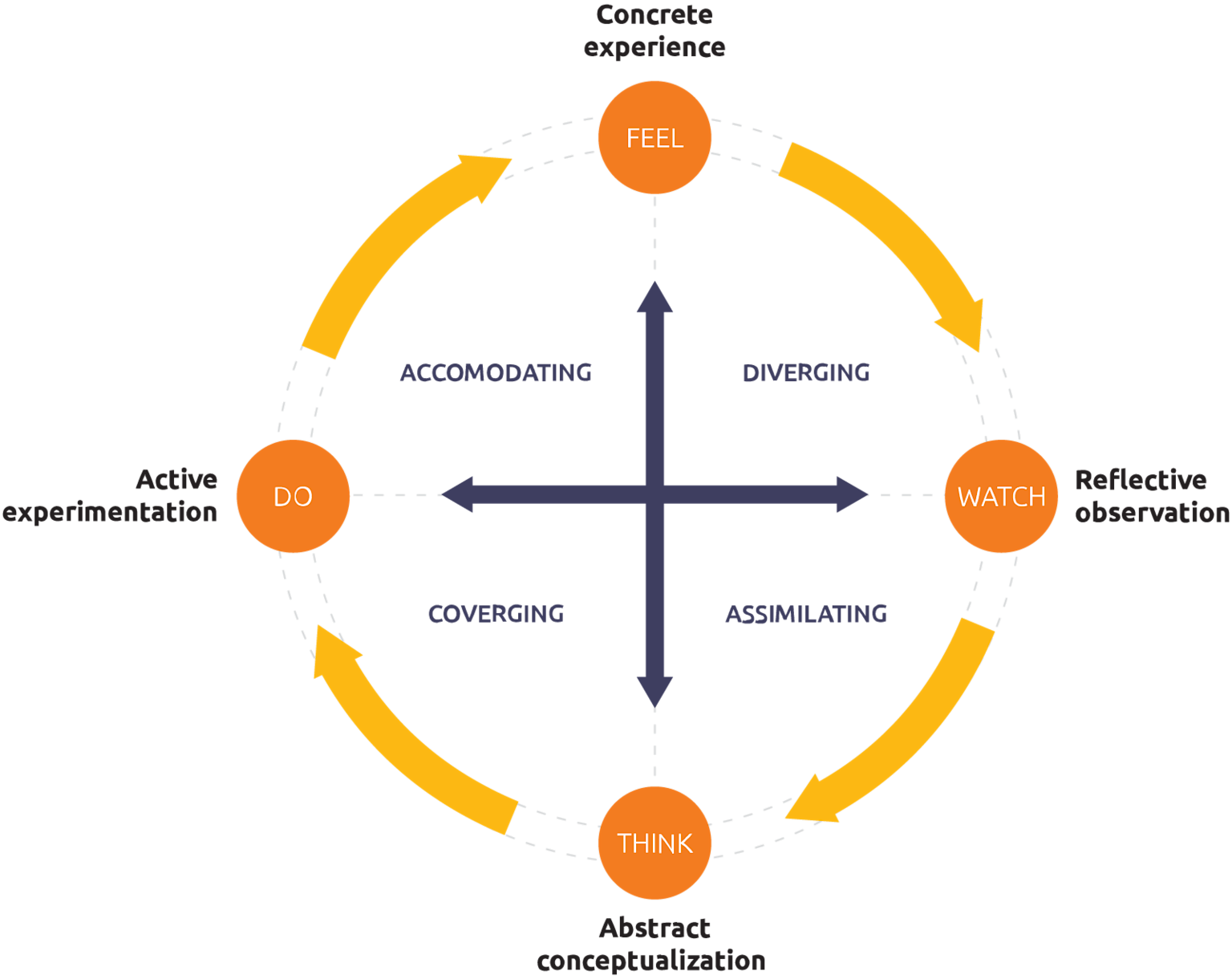
Kolb’s experiential learning cycle showing the four stages of learning and associated learning styles.
2.6 연결주의(2004)
Siemens는 디지털 환경에서 노드 간 연결과 정보 흐름이 학습의 본질이라며 네트워크 이론을 제안했다.1136
3. 신경‧인지 메커니즘
3.1 시냅스 가소성
반복 자극은 시냅스 효율을 증가시켜 장기 기억을 형성한다. 반대로 사용되지 않는 경로는 가지치기(pruning)로 약화된다.61937
3.2 수면과 기억
학습 직후 수면은 해마-대뇌 피질 재활성화를 촉진해 회상을 향상시킨다. 수면이 지연될수록 기억 이득이 감소한다.131422
3.3 의미 맥락과 선행 지식
Ausubel은 선행 조직자를 통해 새로운 정보를 기존 인지구조에 연결할 때 유의미 학습이 촉진된다고 설명했다.383940
4. 현대 학습이론 심층 비교
| 이론 | 핵심 메커니즘 | 장점 | 한계 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 행동주의 | 자극-반응 강화 | 절차 학습, 조건화 설계 | 내적 과정 간과 |
| 인지주의 | 정보처리·스키마 | 사고·기억 모델링 | 사회적 맥락 미흡 |
| 구성주의 | 지식 구성·사회문화 | 실제 문제 해결 | 체계적 평가 어려움 |
| 사회 학습 | 관찰·모방·자기효능감 | 모델 기반 학습 | 동기 변인 복잡 |
| 경험 학습 | 경험 순환 주기 | 직무·성인 교육 적합 | 추상 개념화 난도 |
| 연결주의 | 디지털 네트워크 | 빅데이터·평생학습 | 실증 연구 제한 |
5. 인간 학습 vs 머신러닝
머신러닝은 대규모 데이터에서 패턴을 추출해 일반화를 수행하고, 인간은 희소 경험을 구조화해 추론한다. 인간은 소량 사례로도 개념을 도출하지만, 기계는 수백만 샘플을 요구한다. 두 체계는 보완적 하이브리드 학습 환경을 형성할 수 있다.15414216431744
6. 학습 촉진 조건
- 충분한 수면: 학습 직후 4‒6시간 내 수면이 최적의 공고화를 제공한다.1445
- 유의미 맥락: 실제 문제와 연결된 상황학습은 전이를 극대화한다.464748
- 사회적 참여: 실천 공동체 내 주변적 참여가 전문가 수준으로 이동을 지원한다.4946
- 정서·동기: 긍정적 정서는 주의 집중과 시냅스 강화에 기여한다.1250
7. 종합적 고찰
학습은 신경 가소성·인지 처리·사회적 상호작용·문화적 도구가 결합된 다층적 현상이다. 전통 교실, 디지털 네트워크, 인공지능 환경 모두에서 경험을 구조화하고 반성적 고찰을 촉진할 때 학습의 질이 극대화된다. 교육 설계자는 이러한 통합 관점을 바탕으로 맥락화된 과제, 협력적 활동, 휴식‧수면 관리, 데이터 기반 피드백을 조화롭게 배치해야 한다.433161311
8. 결론
학습을 이해하려면 행동 관찰을 넘어 뇌, 마음, 사회, 기술을 연결하는 통합 프레임이 필요하다. 본 보고서는 정의에서 신경과학, 이론, 기술까지 종합함으로써 “학습이란 무엇인가”에 대한 체계적 해답을 제시하였다. 앞으로도 다학제 연구와 인공지능 활용이 학습 이해와 실천을 한층 심화할 것이다.
Footnotes
-
https://www.managementstudyguide.com/definition-characteristics-and-types-of-learning-in-psychology.htm ↩ ↩2
-
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Long-term_potentiation ↩ ↩2 ↩3
-
https://ko.wikipedia.org/wiki/연결주의_(%ED%95%99%EC%8A%B5%EC%9D%B4%EB%A1%A0) ↩ ↩2 ↩3
-
https://www.verywellmind.com/social-learning-theory-2795074 ↩ ↩2 ↩3
-
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3079906/ ↩ ↩2 ↩3 ↩4
-
https://theelearningcoach.com/learning/10-definitions-learning/ ↩
-
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0896627323002015 ↩ ↩2
-
http://contents2.kocw.or.kr/KOCW/document/2017/stu/parkhyerim/10.pdf ↩
-
http://contents.kocw.or.kr/contents4/document/lec/2013/Chungang/Kangingu1/10.pdf ↩
-
http://contents.kocw.or.kr/contents4/document/lec/2013/Seowon/RohHyelan/4.pdf ↩
-
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kolb’s_experiential_learning ↩
-
https://www.torontomu.ca/experiential-learning/faculty-staff/kolbs-el-cycle/ ↩
-
https://www.edutopia.org/neuroscience-brain-based-learning-neuroplasticity ↩
-
https://www.edulabkorea.com/reference/general.php?ptype=view\&idx=1154\&page=1\&code=general ↩
-
https://ko.wikipedia.org/wiki/데이비드_%EC%98%A4%EC%8A%A4%EB%B2%A8 ↩
-
https://vision-business.consulting/2022/12/30/machine-learning-vs-human-learning/ ↩
-
https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/sleep/articles/10.3389/frsle.2025.1652425/full ↩
-
https://m.cafe.daum.net/moral-study/kED2/3?listURI=%2Fmoral-study%2FkED2 ↩ ↩2
-
https://positivepsychology.com/social-learning-theory-bandura/ ↩
-
https://www.coursebox.ai/ko/blog/yeongyeoljuyi-hagseub-iron ↩
-
https://www.coloradocollege.edu/other/assessment/how-to-assess-learning/learning-outcomes/blooms-revised-taxonomy.html ↩
-
https://marcr.net/marcr-for-career-professionals/career-theory/career-theories-and-theorists/experiential-learning-cycle-david-kolb/ ↩
-
https://www.utica.edu/academic/Assessment/new/Blooms Taxonomy - Best.pdf ↩
-
https://citt.it.ufl.edu/resources/course-development-resources/the-learning-process/designing-the-learning-experience/blooms-taxonomy/ ↩
-
https://www.asecib.ase.ro/mps/Bandura_SocialLearningTheory.pdf ↩
-
https://www.edulabkorea.com/reference/general.php?ptype=view\&idx=697\&page=9\&code=general ↩
-
https://www.mokwon.ac.kr/sw/html/sub05/0502.html?mode=D\&no=35aa7cdf27f82374ff9c1639fa331ebe\&file_id=720175\&category=sw2 ↩
-
https://solportal.ibe-unesco.org/articles/learning-and-memory-how-the-brain-codes-knowledge/ ↩
-
https://translate.google.com/translate?u=https%3A%2F%2Fen.wikipedia.org%2Fwiki%2FLearning\&hl=ko\&sl=en\&tl=ko\&client=srp ↩
-
https://www.teachthought.com/learning-posts/neuroscience-learning/ ↩
-
http://www.educationalneuroscience.org.uk/about-us/what-is-educational-neuroscience/ ↩
-
https://translate.google.com/translate?u=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.britannica.com%2Fscience%2Flearning-theory\&hl=ko\&sl=en\&tl=ko\&client=srp ↩
-
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/14681366.2025.2521458 ↩
-
https://translate.google.com/translate?u=https%3A%2F%2Fknowledgewisdomunderstanding.quora.com%2FWhat-does-it-mean-to-learn\&hl=ko\&sl=en\&tl=ko\&client=srp ↩
-
https://scienceon.kisti.re.kr/srch/selectPORSrchArticle.do?cn=DIKO0012141977 ↩
-
https://goodeducator.tistory.com/entry/행동주의-학습이론의-정의와-예시파블로프의-개-시행착오설-등 ↩
-
http://contents.kocw.or.kr/KOCW/document/2016/cnue/kanghunsik/1.pdf ↩
-
https://experientiallearninginstitute.org/what-is-experiential-learning/ ↩
-
https://citt.it.ufl.edu/resources/course-development-resources/the-learning-process/types-of-learners/kolbs-four-stages-of-learning/ ↩
-
https://www.hee.nhs.uk/sites/default/files/documents/Kolb learning cycle.pdf ↩
-
https://stearnscenter.gmu.edu/knowledge-center/course-and-curriculum-redesign/blooms-taxonomy/ ↩
-
https://www.ebsco.com/research-starters/education/social-learning-theory ↩
-
https://www.ebsco.com/research-starters/education/kolbs-experiential-learning-model ↩
-
https://uwaterloo.ca/centre-for-teaching-excellence/catalogs/tip-sheets/blooms-taxonomy ↩
-
https://practera.com/what-is-the-experiential-learning-theory-of-david-kolb/ ↩
-
https://hr.berkeley.edu/grow/grow-your-community/wisdom-café-wednesday/how-social-learning-theory-works ↩
-
https://mitsloan.mit.edu/ideas-made-to-matter/machine-learning-explained ↩
-
https://www.iso.org/artificial-intelligence/machine-learning ↩
-
https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/artificial-intelligence/articles/10.3389/frai.2022.780405/full ↩
-
https://www.packtpub.com/en-us/learning/how-to-tutorials/is-the-machine-learning-process-similar-to-how-humans-learn/ ↩
-
https://www.ukbiobank.ac.uk/publications/from-youtube-to-the-brain-transfer-learning-can-improve-brain-imaging-predictions-with-deep-learning/ ↩
-
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0278584696001595 ↩
-
https://www.annualreviews.org/content/journals/10.1146/annurev.psych.47.1.173 ↩
-
https://solportal.ibe-unesco.org/articles/neuroplasticity-how-the-brain-changes-with-learning/ ↩
-
https://www.verywellmind.com/what-is-brain-plasticity-2794886 ↩
-
https://science-chemistry-log.tistory.com/entry/4-오수벨의-유의미학습 ↩