너비 우선 탐색 BFS. 파이썬 코딩 테스트
너비 우선 탐색 (BFS) 핸드북
1. BFS란 무엇인가?
**너비 우선 탐색(Breadth-First Search, BFS)**은 그래프나 트리를 탐색하는 가장 기본적이고 중요한 알고리즘 중 하나입니다12. BFS는 시작 노드에서 출발하여 인접한 모든 노드들을 먼저 방문한 후, 그 다음 레벨의 노드들을 방문하는 방식으로 작동합니다34.
BFS의 핵심 특징은 레벨별 탐색입니다. 시작점에서 가까운 노드들부터 차례대로 방문하며, 마치 물에 돌을 던졌을 때 파문이 퍼져나가는 것과 같은 패턴으로 탐색을 진행합니다56.
BFS의 작동 원리
BFS는 큐(Queue) 자료구조를 사용하여 구현됩니다7. 큐의 로 인해 먼저 발견된 노드가 먼저 처리되어 레벨별 탐색이 가능합니다89.
- 초기화: 시작 노드를 큐에 넣고 방문 표시
- 탐색: 큐가 빌 때까지 반복
- 큐에서 노드를 꺼내 현재 노드로 설정
- 현재 노드의 미방문 인접 노드들을 모두 큐에 추가
- 추가된 노드들을 방문 표시
- 종료: 큐가 빌 때까지 반복
2. BFS 구현 방법
2.1 인접 리스트를 이용한 구현
from collections import deque
def bfs_adjacency_list(graph, start):
"""
인접 리스트를 사용한 BFS 구현
시간복잡도: O(V + E)
공간복잡도: O(V)
"""
visited = set()
queue = deque([start])
result = []
while queue:
node = queue.popleft()
if node not in visited:
visited.add(node)
result.append(node)
# 미방문 인접 노드들을 큐에 추가
for neighbor in graph[node]:
if neighbor not in visited:
queue.append(neighbor)
return result2.2 인접 행렬을 이용한 구현
def bfs_adjacency_matrix(matrix, start):
"""
인접 행렬을 사용한 BFS 구현
시간복잡도: O(V²)
공간복잡도: O(V)
"""
n = len(matrix)
visited = [False] * n
queue = deque([start])
result = []
visited[start] = True
while queue:
node = queue.popleft()
result.append(node)
# 모든 인접 노드 확인
for i in range(n):
if matrix[node][i] == 1 and not visited[i]:
visited[i] = True
queue.append(i)
return result2.3 핵심 구현 요소
큐(Queue) 사용: BFS는 반드시 큐 자료구조를 사용해야 합니다710. 파이썬에서는 collections.deque를 사용하여 효율적으로 구현할 수 있습니다1112.
방문 체크: 사이클을 방지하고 무한 루프를 막기 위해 방문한 노드를 추적해야 합니다612. 이는 set이나 boolean 배열을 사용하여 구현할 수 있습니다.
그래프 표현: 인접 리스트나 인접 행렬로 그래프를 표현할 수 있으며, 각각의 시간복잡도가 다릅니다1314.
3. 시간 및 공간 복잡도
3.1 시간 복잡도
BFS의 시간복잡도는 그래프 표현 방식에 따라 달라집니다1516:
- 인접 리스트: O(V + E) - 각 정점과 간선을 한 번씩만 방문17
- 인접 행렬: O(V²) - 모든 정점 쌍을 확인해야 함
여기서 V는 정점의 수, E는 간선의 수입니다1819.
3.2 공간 복잡도
BFS의 공간복잡도는 **O(V)**입니다1517. 이는 다음 요소들로 구성됩니다:
- 큐 저장공간: 최악의 경우 모든 정점이 큐에 저장될 수 있음
- 방문 배열: 모든 정점의 방문 상태를 저장
- 기타 보조 자료구조: 결과 저장 등을 위한 추가 공간
4. BFS vs DFS 비교
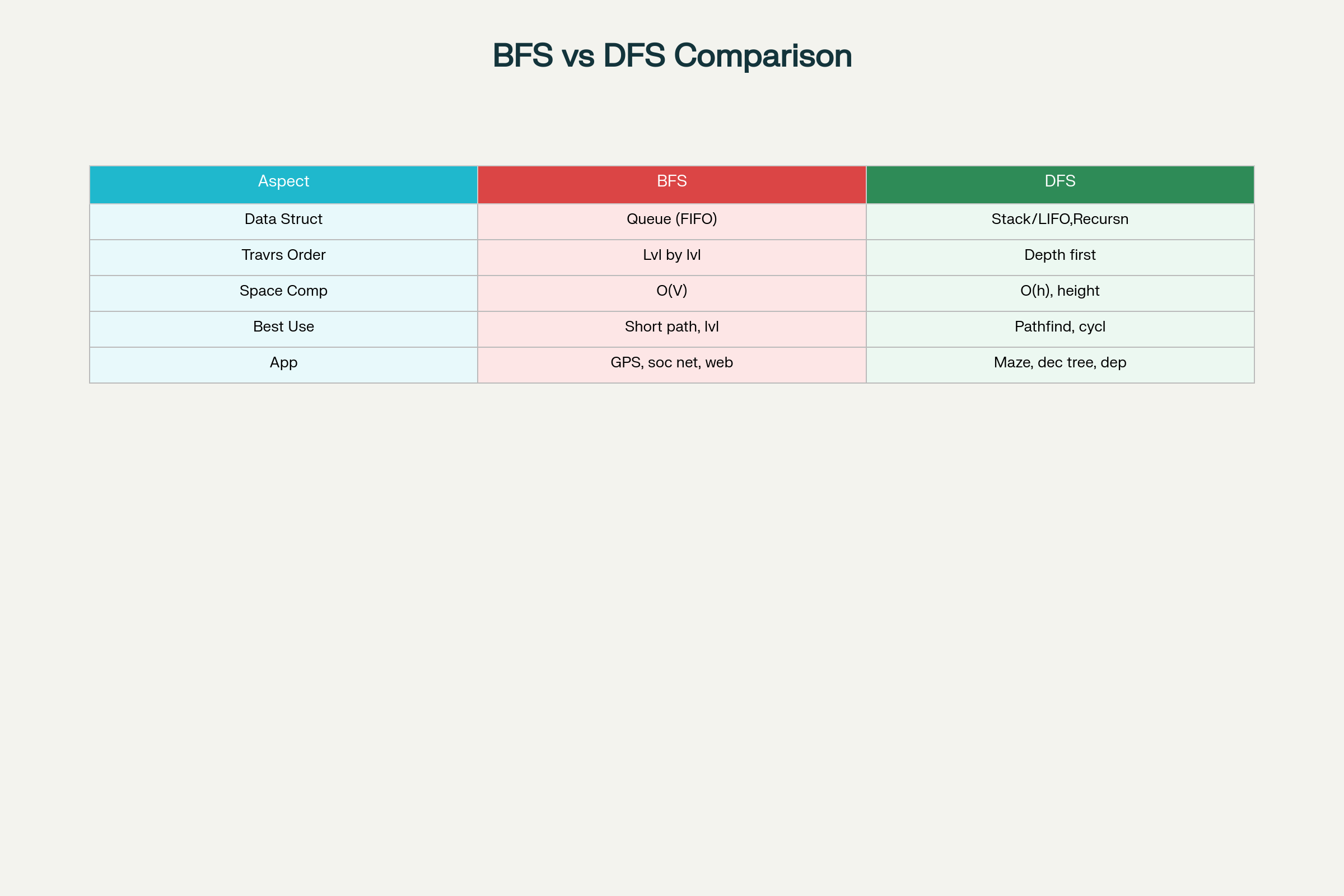
BFS vs DFS: Key Differences and Applications
5. BFS의 주요 응용 분야
5.1 최단 경로 찾기
BFS는 가중치가 없는 그래프에서 최단 경로를 찾는 가장 효율적인 방법입니다2224. 레벨별로 탐색하는 특성상 처음 목표에 도달하는 경로가 항상 최단 경로입니다623.
def bfs_shortest_path(graph, start, end):
"""BFS를 이용한 최단 경로 찾기"""
if start == end:
return [start], 0
visited = set()
queue = deque([(start, [start])])
visited.add(start)
while queue:
node, path = queue.popleft()
for neighbor in graph[node]:
if neighbor not in visited:
new_path = path + [neighbor]
if neighbor == end:
return new_path, len(new_path) - 1
visited.add(neighbor)
queue.append((neighbor, new_path))
return None, -15.2 레벨 순서 트리 순회
이진 트리의 레벨 순서 순회는 BFS의 대표적인 응용 사례입니다2526. 트리의 각 레벨을 순서대로 방문하여 계층적 구조를 파악할 수 있습니다2728.
def bfs_level_order_traversal(root):
"""이진 트리의 레벨 순서 순회"""
if not root:
return []
result = []
queue = deque([root])
while queue:
level_size = len(queue)
current_level = []
for _ in range(level_size):
node = queue.popleft()
current_level.append(node.val)
if node.left:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right:
queue.append(node.right)
result.append(current_level)
return result5.3 연결 요소 찾기
BFS는 **그래프의 연결 요소(Connected Components)**를 찾는 데 효과적으로 사용됩니다2930. 각 연결 요소는 서로 도달 가능한 노드들의 집합입니다3132.
5.4 미로 해결
BFS는 미로에서 최단 경로를 찾는 데 널리 사용됩니다3334. 2차원 격자에서 시작점부터 목표점까지의 최소 이동 거리를 계산할 수 있습니다3536.
5.5 실제 응용 사례
- GPS 네비게이션: 최단 경로 찾기3738
- 소셜 네트워크: 친구 추천, 관계 분석37
- 웹 크롤링: 링크를 따라 페이지 탐색3937
- 네트워크 브로드캐스팅: 데이터 전파 경로 최적화37
6. 코딩 테스트에서의 BFS 패턴
6.1 주요 문제 패턴
BFS는 코딩 테스트에서 **가장 높은 ROI(투자 대비 효과)**를 가지는 알고리즘 중 하나입니다4041. 다음과 같은 패턴의 문제에서 자주 출제됩니다:
6.2 문제 해결 접근법
- “최단”, “최소”, “shortest”
- “level”, “레벨별”
- “동시에”, “한 번에”
- “flood fill”, “전파”
6.3 구현 팁
- 큐 사용:
collections.deque활용1112 - 방문 체크:
set또는boolean배열 사용 - 레벨 구분: 필요시 레벨별로 노드 개수 추적
- 격자 문제: 방향 벡터 활용으로 인접 셀 탐색
7. BFS의 특성과 제한사항
7.1 장점
7.2 제한사항
8. 결론
BFS는 그래프 탐색의 기초가 되는 중요한 알고리즘으로, 최단 경로 찾기, 레벨 순서 순회, 연결 요소 찾기 등 다양한 분야에서 활용됩니다12. 특히 코딩 테스트에서는 높은 출제 빈도를 보이며, 큐 자료구조를 기반으로 한 체계적인 구현이 핵심입니다4041.
BFS의 O(V + E) 시간복잡도와 O(V) 공간복잡도를 이해하고, 문제의 특성에 따라 DFS와 적절히 구분하여 사용하는 것이 중요합니다1617. 실제 구현에서는 큐, 방문 체크, 그래프 표현 방식을 정확히 이해하여 다양한 문제 상황에 대응할 수 있어야 합니다1112.
Footnotes
-
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/dsa/breadth-first-search-or-bfs-for-a-graph/ ↩ ↩2 ↩3
-
https://celerdata.com/glossary/breadth-first-search-bfs ↩ ↩2
-
https://www.hackerearth.com/practice/algorithms/graphs/breadth-first-search/tutorial/ ↩ ↩2
-
https://www.simplilearn.com/tutorials/data-structure-tutorial/bfs-algorithm ↩
-
https://stephan-osterburg.gitbook.io/coding/coding/leetcode/queue-and-stack/queue-and-bfs ↩
-
https://library.fiveable.me/data-structures/unit-11/breadth-first-search-bfs-algorithm/study-guide/3ykxmer0DnvoLRNV ↩
-
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/39731498/why-does-the-bfs-algorithm-use-a-queue ↩
-
https://www.datacamp.com/tutorial/breadth-first-search-in-python ↩ ↩2 ↩3
-
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/python/python-program-for-breadth-first-search-or-bfs-for-a-graph/ ↩ ↩2 ↩3 ↩4
-
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/c/c-program-for-breadth-first-search-or-bfs-for-a-graph/ ↩
-
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/dsa/implementation-of-bfs-using-adjacency-matrix/ ↩
-
https://ds1-iiith.vlabs.ac.in/exp/breadth-first-search/analysis/time-and-space-complexity-of-bfs.html ↩ ↩2 ↩3
-
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/dsa/time-and-space-complexity-of-dfs-and-bfs-algorithm/ ↩ ↩2
-
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/dsa/time-and-space-complexity-of-breadth-first-search-bfs/ ↩ ↩2 ↩3 ↩4
-
https://www.thecodeofnumbers.com/post/unraveling-the-mathematical-foundations-of-breadth-first-search-bfs ↩
-
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/3332947/what-are-the-practical-factors-to-consider-when-choosing-between-depth-first-sea ↩ ↩2 ↩3
-
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/dsa/when-to-use-dfs-or-bfs-to-solve-a-graph-problem/ ↩ ↩2 ↩3
-
https://codesignal.com/learn/courses/mastering-graphs-in-python/lessons/finding-the-shortest-path-in-graphs-with-bfs-algorithm ↩ ↩2 ↩3 ↩4
-
https://library.fiveable.me/introduction-algorithms/unit-8/breadth-first-search-bfs-algorithm-applications/study-guide/qLi7YOuQAJt0zkHC ↩ ↩2 ↩3 ↩4
-
https://courses.grainger.illinois.edu/cs374al1/sp2023/slides/17-shortest-paths.pdf ↩ ↩2
-
https://www.enjoyalgorithms.com/blog/level-order-traversal-of-binary-tree/ ↩ ↩2 ↩3
-
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/dsa/level-order-tree-traversal/ ↩ ↩2
-
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/level-order-traversal-in-a-binary-tree ↩ ↩2
-
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/dsa/print-level-order-traversal-line-line/ ↩
-
https://math.stackexchange.com/questions/2699333/finding-connected-components-in-a-graph-using-bfs ↩ ↩2
-
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/dsa/connected-components-in-an-undirected-graph/ ↩ ↩2
-
https://gmlwjd9405.github.io/2018/08/16/algorithm-connected-component.html ↩
-
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/dsa/count-number-of-ways-to-reach-destination-in-a-maze-using-bfs/ ↩ ↩2
-
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/16366448/maze-solving-with-breadth-first-search ↩
-
https://www.iquanta.in/blog/applications-of-bfs-or-breadth-first-search/ ↩ ↩2 ↩3 ↩4
-
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/dsa/applications-of-breadth-first-traversal/ ↩
-
https://www.scaler.com/topics/breadth-first-search-python/ ↩
-
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/dfs-bfs-coding-interview-3-steps-success-jimmy-zhang-hldgf ↩ ↩2 ↩3
-
https://igotanoffer.com/blogs/tech/breadth-first-search-interview-questions ↩
-
https://www.reddit.com/r/leetcode/comments/1deb3yi/dfs_and_bfs_3_steps_to_success/ ↩